Diabetes not only impairs normal tissue repair but also compromises the natural wound healing process.
It is now understood that diabetes causes a slowing in wound healing, making recovery more challenging than usual.
Sadly, but unavoidably, minor injuries like cuts, burns, and wounds are a part of life. Yet, these injuries might cause major health problems for diabetics. Many diabetics experience wounds that either never heal, heal poorly, or heal slowly. An infection may sometimes develop.
An infection can spread to nearby bone and tissue or farther away regions of the body. In rare instances, an infection can be lethal or life-threatening if a person does not obtain immediate care.
Slow healing can have a negative impact on a person's general health and quality of life, even when an infection does not manifest in a wound. Cuts or injuries to the legs or feet can make walking painful and make exercise painful.
Keeping blood sugar levels under control is crucial for diabetics to lower their risk of problems like foot ulcers and slow-healing wounds.
Why is diabetes a factor in the slow healing of wounds?
This illness raises the risk of developing chronic sores, such as ulcerative lesions of the lower limbs, which, if left untreated after complications brought on by potential infections, may even need amputation.
These occurrences in diabetes would appear to be brought on by inflammatory processes that can result from alterations in the body's capacity to regulate the production of cytokines, essential mediators of intercellular communication that serve a variety of purposes in our bodies.
A deficiency already exists at the level of the very early phases of the wound healing process if the migration of the cells responsible for tissue repair is slowed down or disrupted.
Parallel to this, diabetic microangiopathy is a condition where blood vessels are partially or completely blocked. This might affect tissue healing in the lower limbs by reducing the amount of oxygen that can be transported through the blood circulation.
Research Study demonstrates a direct link between blood sugar levels and wound healing. Diabetes affects the body's capacity to create or react to insulin, a hormone that enables cells to absorb and utilize blood glucose for energy. It is more difficult for the body to control blood glucose levels as a result of this insulin disturbance.
White blood cell functionality is hampered when blood glucose levels are chronically elevated. In order for the immune system to function, white blood cells are essential. The body's capacity to combat infections and heal wounds is decreased when white blood cells are unable to operate properly.
Uncontrolled diabetes may also have an impact on blood flow, which makes it more challenging for the body to provide nutrients to wounds. As a result, the injuries may recover slowly or not at all.
Diabetes can also result in diabetic neuropathy, which can hinder the healing of wounds. Uncontrolled blood sugar levels might harm the local nerves and dull the area's senses.
This might imply that persons with diabetes who have foot damage might not be aware of the injury.
How should wounds be treated if you have diabetes?
Remember that when we have diabetes, our body is unable to manage the amount of glucose in our blood.
A person might not seek medical attention if they are unaware of an injury, which might cause the wound to deteriorate. The likelihood of infection increases dramatically when sluggish healing and decreased feeling are present.
Risk elements might consist of:
- Infected toenails
- Charcot's foot is one example of a foot abnormality
- Reduced sweating
- Cracked and parched skin
Wound treatment
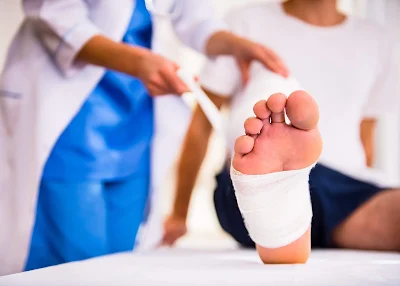
Cleaning the wound and wrapping it in a fresh bandage is the first procedure, which should be done each day.
People with diabetes may want to consider dressing in shoes and socks when moving about, especially if a wound has occurred. Infection risk is higher when barefoot.
If a wound appears on your foot and it doesn't heal, get help. Antibiotics are frequently required to treat infections, and if the wound is serious, hospitalization may also be necessary.
Remember to not apply pressure on the wound using bandages.
It is essential to make sure the bandages are not putting too much pressure to the wounds when applying the dressing since doing so might harm the skin and worsen the wound's state.
Foot care for diabetes
- Gently cutting the toenails
- Putting on cozy shoes
- Regular examination of the feet and inside of the shoes
- Getting the feet examined by a doctor at each appointment
- Everyday foot washing
- Applying moisturizer after patting the skin dry
- Avoiding barefoot travel
Glucose control
Severe wounds that do not heal are less common in those who control their blood sugar levels.
Those with type 2 diabetes have more alternatives, however those with type 1 diabetes will always need to take insulin to maintain their blood sugar. Together with using insulin and other drugs, changing one's lifestyle to include a healthy diet, frequent exercise, and achieving or maintaining a reasonable weight may significantly lower one's blood sugar levels.
Even managing diabetes without medication may be possible with certain lifestyle modifications.
A diet low in carbohydrates can help those with type 1 or type 2 diabetes. A doctor can recommend a meal plan that contains the precise amount of carbohydrates that a person should have each day. This may be useful.
When to visit a doctor after wounding:
If you encounter any of the following symptoms, you should speak with your doctor or another qualified professional immediately.
- Burning feeling that never stops
- Sensation is lost somewhat.
- Severe and ongoing discomfort
- Swelling in the area impacted
- Tingling
The infection may progress rapidly to muscle and bone if an untreated wound becomes infected. Physicians refer to condition as osteomyelitis.
Untreated wound infections can advance to the point of gangrene if they grow and are left untreated. Those who lose limbs due to diabetes frequently have to have them amputated due to gangrene.

0 Comments
Post a Comment
Share your views